Stationary Steam Engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from
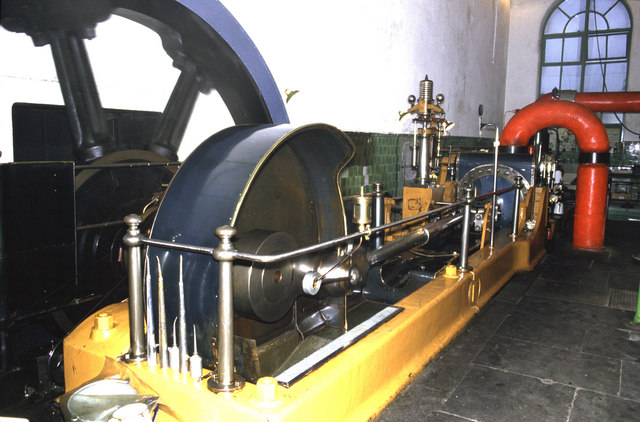
 There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by
the layout of the cylinders and
There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by
the layout of the cylinders and 
Old Engine House, List of Museums
– ''examples of stationary steam engines preserved in the UK (with pictures and links)''
– ''comprehensive coverage of stationary steam engines in their original locations, working and non-working, in many countries''
preserved stationary steam engines
– ''includes lesser-known museums containing such engines (UK)''
Steamers steam engine forum
– ''Questions and answers about old steam engines, traction engines'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Stationary Steam Engine Stationary steam engines Steam engines Stationary engines
locomotive engines
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, motor coach, railcar or power car; the u ...
used on railways
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
, traction engine
A traction engine is a steam engine, steam-powered tractor used to move heavy loads on roads, plough ground or to provide power at a chosen location. The name derives from the Latin ''tractus'', meaning 'drawn', since the prime function of any t ...
s for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam car
A steam car is a car (automobile) propelled by a steam engine. A steam engine is an external combustion engine (ECE) in which the fuel is combusted outside of the engine, unlike an internal combustion engine (ICE) in which fuel is combusted ins ...
s (and other motor vehicles), agricultural engine
A traction engine is a steam-powered tractor used to move heavy loads on roads, plough ground or to provide power at a chosen location. The name derives from the Latin ''tractus'', meaning 'drawn', since the prime function of any traction engine ...
s used for ploughing or threshing, marine engines, and the steam turbines used as the mechanism of power generation for most nuclear power plants.
They were introduced during the 18th century and widely made for the whole of the 19th century and most of the first half of the 20th century, only declining as electricity supply and the internal combustion engine became more widespread.
Types of stationary steam engine

 There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by
the layout of the cylinders and
There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by
the layout of the cylinders and crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting ...
:
* Beam engines have a rocking beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
providing the connection between the vertical cylinder and crankshaft.
*Table engine
A table engine is a variety of stationary steam engine where the cylinder is placed on top of a table-shaped base, the legs of which stand on the baseplate which locates the crankshaft bearings. The piston rod protrudes from the top of the cylinder ...
s have the crosshead above the vertical cylinder and the crankshaft below.
*Horizontal engines have a horizontal cylinder.
*Vertical engines have a vertical cylinder.
*Inclined engines have an inclined cylinder.
*Undertype engines are distinguished by having a locomotive-style boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, centr ...
over top of a horizontal engine.
Stationary engines may be classified by secondary characteristics as well:
* High-speed engines are distinguished by fast-acting valves.
*Corliss engine
A Corliss steam engine (or Corliss engine) is a steam engine, fitted with rotary valves and with variable valve timing patented in 1849, invented by and named after the American engineer George Henry Corliss of Providence, Rhode Island.
Engines f ...
s are distinguished by special rotary valve gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing ...
.
* Uniflow engines have admission valves at the cylinder heads and exhaust ports at the midpoint.
When stationary engines had multiple cylinders, they could be classified as:
*Simple engines, with multiple identical cylinders operating on a common crankshaft.
*Compound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struc ...
engines which use the exhaust from high-pressure cylinders to power low-pressure cylinders.
An engine could be run in simple or condensing mode:
* Simple mode meant the exhaust gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an ...
left the cylinder and passed straight into the atmosphere
* In condensing mode, the steam was cooled in a separate cylinder, and changed from vapour to liquid water, creating a vacuum that assisted with the motion. This could be done with a water-cooled plate that acted as a heat sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, th ...
, or pumping-in a spray of water.
Stationary engines may also be classified by their application:
*Pumping engines are found in pumping station
Pumping stations, also called pumphouses in situations such as drilled wells and drinking water, are facilities containing pumps and equipment for pumping fluids from one place to another. They are used for a variety of infrastructure system ...
s.
*Mill engines to power textile mill
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods ...
s
*Winding engine
A winding engine is a stationary engine used to control a cable, for example to power a mining hoist at a pit head. Electric hoist controllers have replaced proper winding engines in modern mining, but use electric motors that are also tradit ...
s power various types of hoists.
*Refrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, ht ...
engines are typically coupled to ammonia compressors.
Stationary engines could be classified by the manufacturer
*Boulton & Watt
Boulton & Watt was an early British engineering and manufacturing firm in the business of designing and making marine and stationary steam engines. Founded in the English West Midlands around Birmingham in 1775 as a partnership between the Eng ...
*George Saxon & Co
George Saxon & Co was an English engineering company that manufactured stationary steam engines. It was based in the Openshaw district of Greater Manchester, Manchester. The company produced large steam-driven engines for power stations and la ...

History
In order of evolution: *Savery Savery is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Constance Savery (1897-1999), English author
* Gil Savery (1917-2018), American journalist
* Henry Savery (1791–1842), Australian novelist
* Jan Savery (1589–1654), Flemish paint ...
atmospheric engine (1700)
* Newcomen engine
The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is often referred to as the Newcomen fire engine (see below) or simply as a Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam drawn into the cylinder, thereby creati ...
(1712)
* Watt engine
The Watt steam engine design became synonymous with steam engines, and it was many years before significantly new designs began to replace the basic Watt design.
The first steam engines, introduced by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, were of the "at ...
(1775)
* Hornblower (1781)
* Trevithick Trevithick ( ) is a Cornish surname, and may refer to:
* Francis Trevithick (1812–1877), one of the first locomotive engineers of the London and North Western Railway
* Jonathan Trevethick (1864–1939), New Zealand politician
* Paul Trevithic ...
(1799)
* Woolf
Adeline Virginia Woolf (; ; 25 January 1882 28 March 1941) was an English writer, considered one of the most important modernist 20th-century authors and a pioneer in the use of stream of consciousness as a narrative device.
Woolf was born i ...
(1804)
* Cornish engine (1812)
* McNaught'ed compound beam engines (1845)
* Corliss engine
A Corliss steam engine (or Corliss engine) is a steam engine, fitted with rotary valves and with variable valve timing patented in 1849, invented by and named after the American engineer George Henry Corliss of Providence, Rhode Island.
Engines f ...
(1859)
* Porter-Allen engine (1862)
* Uniflow engine Todd's (1885)
* Steam turbine (1889)
See also
* Boilers *Centrifugal governor
A centrifugal governor is a specific type of governor with a feedback system that controls the speed of an engine by regulating the flow of fuel or working fluid, so as to maintain a near-constant speed. It uses the principle of proportional con ...
*Lineshaft
A line shaft is a power-driven rotating shaft for power transmission that was used extensively from the Industrial Revolution until the early 20th century. Prior to the widespread use of electric motors small enough to be connected directly to e ...
*Belt
Belt may refer to:
Apparel
* Belt (clothing), a leather or fabric band worn around the waist
* Championship belt, a type of trophy used primarily in combat sports
* Colored belts, such as a black belt or red belt, worn by martial arts practit ...
* List of steam energy topics
* Live steam
* Steam fair
* Stationary engine
*Steam donkey
A steam donkey or donkey engine is a steam-powered winch once widely used in logging, mining, maritime, and other industrial applications.
Steam powered donkeys were commonly found on large metal-hulled multi-masted cargo vessels in the later ...
* Preserved stationary steam engines
References
Bibliography
*Buchanan, R. A., and Watkins, George, ''The Industrial Archaeology of the Stationary Steam Engine'', London, 1976, * * *Watkins, George, ''Stationary Steam Engines of Great Britain'', Landmark Publishing, various ISBNs :Vol 1, Yorkshire (2000) :Vol 2, Scotland and Northern England (2000) :Vols 3:1, 3:2, Lancashire (2001) :Vol 4, Wales, Cheshire,& Shropshire (2002) :Vol 5, The North Midlands (2002) :Vol 6, The South Midlands (2003) :Vol 7, The South and South West (2003) :Vol 8, Greater London and the South East (2003) :Vol 9, East Anglia & adjacent counties (2004) :Vol 10, Marine Engines (and readers' notes, indexes to the series etc) (2005) This series reproduces some 1,500 images from the Steam Engine Record made by George Watkins between 1930 and 1980, which is now in the Watkins Collection at English Heritage's National Monuments Record at Swindon,Wilts
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
.
External links
* *Old Engine House, List of Museums
– ''examples of stationary steam engines preserved in the UK (with pictures and links)''
– ''comprehensive coverage of stationary steam engines in their original locations, working and non-working, in many countries''
preserved stationary steam engines
– ''includes lesser-known museums containing such engines (UK)''
Steamers steam engine forum
– ''Questions and answers about old steam engines, traction engines'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Stationary Steam Engine Stationary steam engines Steam engines Stationary engines